40 What Is Design Thinking?
This chapter is designed to help you to:
● Identify, analyze, synthesize, evaluate and apply knowledge and theories describing the essential competencies of design thinking in a wide range of contexts
● Think creatively about design problems and opportunities by developing and communicating insights using brainstorming and rapid prototyping methods
● Assess and experience the impact of human-centred design research using interviews, user experience design, and user testing
The Design Thinking Method and Mindset
Design Thinking is a Method
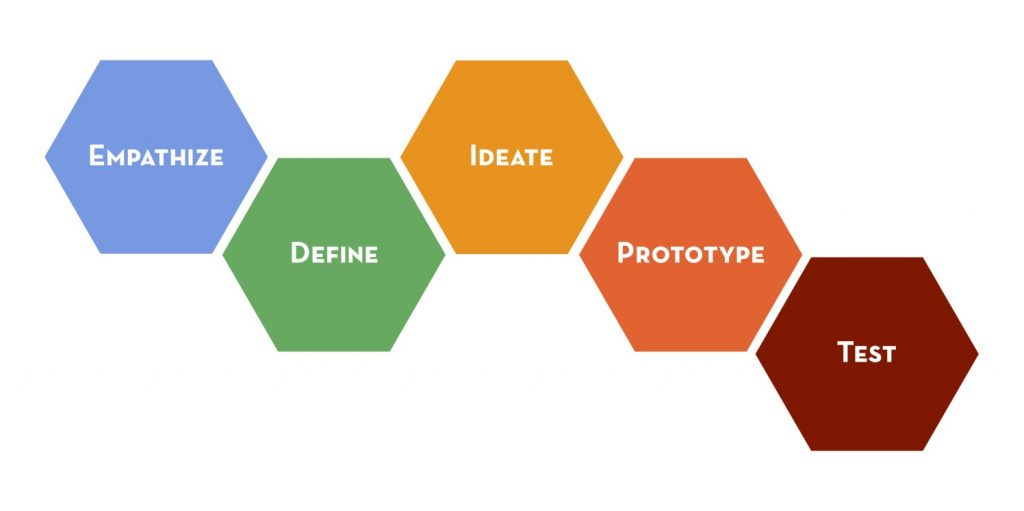
Design thinking is a methodology for creative problem solving. It’s a structured and cyclical approach to generating and evolving ideas. It has five phases that help navigate the development from identifying a design challenge to finding and building a solution. Those phases include: empathizing, defining the problem, ideating solutions, prototyping ideas, and testing with users.
Design thinking promotes a human-centred approach to innovation. The process begins by developing deep empathy and understanding of the needs and motivations of people.
It’s also experimental. Design thinking gives you permission to fail and to learn from your mistakes, because you come up with new ideas, get feedback on them, then iterate and improve on them.
You can use design thinking to approach any challenge. Whether the problem is big or small, regardless of whether it is a personal, creative, social, commercial, technical or creative problem.
In a nutshell, the five basic phases of the design thinking method include:
- Empathize with users (learn about and understand the people you’re designing for)
- Define the design problem (identify the users’ needs and focus on a design challenge)
- Ideate (generating and evaluating creative ideas)
- Prototype solutions (turning insights and ideas into tangible models)
- Test (evaluating and evolving solutions by gathering actionable feedback from users)
Design Thinking is a Mindset
Design thinking is about believing we can make a difference, and having an intentional process in order to get to new, relevant solutions that create positive impact. Design Thinking gives you faith in your creative abilities and a process for transforming difficult challenges into opportunities for design.
Using a design thinking approach to innovation means adopting an optimistic mindset. This approach encourages the fundamental belief that we all can create change, no matter how big a problem, how little time or how small a budget we have to work with. No matter what constraints exist around you, designing can be an enjoyable process because it instills confidence that new, better things are possible and that you can make them happen.
Design thinkers see problems as opportunities for design in disguise.
Attributions: material from the following open source text was adapted and integrated into this chapter
“Design Thinking for Educators” IDEO. Circa 2013. CC BY-NC-SA 3.0
Design Thinking Copyright © by Sidneyeve Matrix is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
